INFORMATICS UNIT 2 NOTES
UNIT 2 INFORMATICS NOTES
⭕ Drivers of digital business
Drivers of digital business refer to the key factors, technologies, and trends that enable and accelerate digital transformation and innovation in organizations. These drivers facilitate the creation of new business models, revenue streams, and customer experiences.
Drivers of digital business refer to the key factors, technologies, and trends that enable and accelerate digital transformation and innovation in organizations. These drivers facilitate the creation of new business models, revenue streams, and customer experiences.
*Key Benefits:*
1. Enhanced Customer Experience
2. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
3. Improved Decision-Making
4. New Revenue Streams and Business Models
5. Competitive Advantage
6. Innovation and Growth
⭕BIG DATA ANALYTICS
Big Data refers to the vast amounts of structured and unstructured data generated from various sources, including:
1. Social media
2. IoT devices
3. Sensors
4. Transactions
5. Logs
6. Clickstream data
7. Text data
8. Images
9. Videos
⭕ Here are some things to know about big data analytics:
•
• Data sources
Big data can come from a variety of sources, including social media, mobile, email, web, and smart devices.
•
• Data types
Big data can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
•
• Tools
Big data analytics uses tools like business intelligence (BI) systems and tools to help organizations collect and analyze data.
•
• Techniques
Big data analytics uses statistical analysis techniques like clustering and regression, along with newer tools.
•
• Types
There are four main types of big data analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive.
•
• Benefits
Big data analytics can help businesses understand product viability, keep up with trends, and develop and market new products and services.
•
• History
The term "big data" was first used in the mid-1990s to describe the increasing volume of data being stored and used by organizations.
⭕
*Applications of Big Data and Analytics:*
1. Healthcare
2. Finance
3. Retail
4. Marketing
5. Manufacturing
6. Government
7. Transportation
8. Education
⭕ Cloud Computing and StoStorage


*Cloud Computing:*
Cloud computing is a model of delivering computing services over the internet, on-demand and pay-per-use basis.
Key Characteristics:
1. On-demand self-service
2. Broad network access
3. Resource pooling
4. Rapid elasticity
5. Measured service
Characteristics of Cloud Computing

*Cloud Computing Benefits:*
1. Scalability
2. Flexibility
3. Cost-effectiveness
4. Reliability
5. Security
6. Collaboration
7. Automatic software updates
*Cloud Storage:*
Cloud storage is a model of storing data online, accessible from anywhere, and scalable.
*Cloud Storage Benefits:*
1. Scalability
2. Accessibility
3. Reliability
4. Security
5. Collaboration
6. Automatic backups
7. Disaster recovery

The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data.
_Key Characteristics:_
1. Digitalization of business processes
2. Use of digital technologies (cloud, AI, IoT, blockchain)
3. Online presence and digital channels
4. Data-driven decision-making
5. Digital products and services
6. E-commerce and digital payments
7. Digital marketing and customer engagement
8. Continuous innovation and disruption
⭕ OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES OF DIGITAL BUSINESS ⭕
*Opportunities of Digital Business:*
1. Increased reach and accessibility
2. Improved customer engagement and experience
3. Enhanced data-driven decision-making
4. Increased efficiency and productivity
5. New revenue streams and business models
6. Competitive advantage through innovation
7. Real-time market feedback and adaptation
8. Global market access and expansion
*Challenges of Digital Business:*
1. Cybersecurity threats and data breaches
2. Rapid technological changes and obsolescence
3. Intense competition and market saturation
4. Managing digital transformation and cultural change
5. Ensuring data quality and integrity
6. Balancing personalization and privacy concerns
7. Managing digital risks and liabilities
8. Keeping up with evolving regulatory frameworks
⭕Digital banking
Digital banking, also known as online banking or e-banking, refers to the provision of banking services through digital channels such as the internet, mobile devices, and other electronic platforms.
*Types of Digital Banking:*
1. Online Banking (web-based)
2. Mobile Banking (app-based)
3. Mobile Wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay)
4. Digital-Only Banks (neobanks)
5. Virtual Banking (virtual assistants)
6. Social Media Banking
7. SMS Banking
8. Chatbot Banking
*Digital Banking Services:*
1. Account management (view balances, transactions)
2. Fund transfers (local and international)
3. Bill payments
4. Loan applications
5. Credit card management
6. Investment services
7. Insurance services
8. Financial planning and advisory
*Benefits of Digital Banking:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
⭕ Digital banking
Digital banking, also known as online banking or e-banking, refers to the provision of banking services through digital channels such as the internet, mobile devices, and other electronic platforms.
*Types of Digital Banking:*
1. Online Banking (web-based)
2. Mobile Banking (app-based)
3. Mobile Wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay)
4. Digital-Only Banks (neobanks)
5. Virtual Banking (virtual assistants)
6. Social Media Banking
7. SMS Banking
8. Chatbot Banking
*Digital Banking Services:*
1. Account management (view balances, transactions)
2. Fund transfers (local and international)
3. Bill payments
4. Loan applications
5. Credit card management
6. Investment services
7. Insurance services
8. Financial planning and advisory
*Benefits of Digital Banking:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
⭕ONLINE BANKING
Online banking, also known as internet banking or e-banking, allows users to manage their financial accounts and conduct banking transactions through the internet.
*Benefits of Online Banking:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
*Online Banking Features:*
1. User-friendly interface
2. Secure login and authentication
3. Transaction history and statements
4. Fund transfer and payment options
5. Account alerts and notifications
6. Budgeting and financial planning tools
7. Investment tracking and analysis
8. Customer support and chat services
⭕ MOBILE BANKING
Mobile banking refers to the provision of banking services through mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices.
*Key Features:*
1. Account management
2. Fund transfers
3. Bill payments
4. Loan applications
5. Credit card management
6. Investment services
7. Insurance services
8. Financial planning and advisory
*Benefits:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
⭕TELEBANKING
Telebanking , also known as phone banking, refers to the provision of banking services over the telephone.
*Telebanking Services:*
1. Account balance inquiry
2. Fund transfers
3. Bill payments
4. Loan applications
5. Credit card management
6. Investment services
7. Insurance services
8. Financial planning and advisory
*Benefits of Telebanking:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
⭕Automatic Clearing House (ACH)
Automatic Clearing House (ACH) is a network that facilitates electronic funds transfers (EFTs) between banks and financial institutions.
*Key Features:*
1. Electronic payment processing
2. Batch processing
3. High-volume transactions
4. Low-cost transactions
5. Secure and reliable
*Types of ACH Transactions:*
1. Direct Deposit (payroll, benefits)
2. Direct Payment (bill payments, tuition)
3. Electronic Checks (e-checks)
4. Recurring Payments (subscriptions, memberships)
5. One-time Payments (online purchases)
⭕ BHIM
BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money) is a mobile payment application developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) to facilitate electronic payments and promote digital transactions in India.
*Key Features:*
1. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) based
2. Scan and Pay using QR code
3. Send and Receive money using Virtual Payment Address (VPA)
4. Bill payments and utility payments
5. Support for multiple languages
6. Integration with various banks
7. Transaction limits: ₹10,000 per transaction, ₹20,000 daily
*Benefits:*
1. Convenient and easy to use
2. Fast and secure transactions
3. No need to carry cash or cards
4. Wide acceptance across merchants
5. Low transaction fees
6. Promotes digital financial inclusion
*Transaction Types:*
1. Person-to-Person (P2P)
2. Person-to-Merchant (P2M)
3. Bill payments
4. Utility payments
5. Online shopping
*Security Features:*
1. Two-factor authentication
2. Encryption
3. Secure socket layer (SSL)
4. Virtual Payment Address (VPA)
5. PIN/password protection
*Participating Banks:*
1. State Bank of India
2. HDFC Bank
3. ICICI Bank
4. Axis Bank
5. Bank of Baroda
6. And many more
⭕UPI
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is a real-time payment system developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) to facilitate inter-bank transactions.
*Key Features:*
1. Instant fund transfers
2. Real-time transactions
3. Single-click payments
4. Virtual Payment Address (VPA)
5. Two-factor authentication
6. Multiple bank account linking
7. Transaction limits: ₹1 lakh per transaction, ₹1 lakh daily
*Benefits:*
1. Convenient and easy to use
2. Fast and secure transactions
3. No need to share bank account details
4. Wide acceptance across merchants
5. Low transaction fees
6. Promotes digital financial inclusion
*Transaction Types:*
1. Person-to-Person (P2P)
2. Person-to-Merchant (P2M)
3. Bill payments
4. Utility payments
5. Online shopping
*Security Features:*
1. Two-factor authentication
2. Encryption
3. Secure socket layer (SSL)
4. Virtual Payment Address (VPA)
5. PIN/password protection
*Participating Banks:*
1. State Bank of India
2. HDFC Bank
3. ICICI Bank
4. Axis Bank
5. Bank of Baroda
6. And many more
*UPI Apps:*
1. BHIM
2. Google Pay
3. PhonePe
4. Paytm
5. Amazon Pay
6. WhatsApp Pay
⭕DIGITAL WALLET

A digital wallet, also known as an e-wallet, is a software-based storage solution that securely stores payment information and allows users to make transactions online or offline.
*Types of Digital Wallets:*
1. Mobile wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay)
2. Online wallets (e.g., PayPal, Amazon Pay)
3. Desktop wallets (e.g., Bitcoin Core)
4. Hardware wallets (e.g., Ledger, Trezor)
5. Cryptocurrency wallets (e.g., Coinbase, MetaMask)
*Features:*
1. Payment storage (credit/debit cards, bank accounts)
2. Transaction history
3. Password protection
4. Two-factor authentication
5. Encryption
6. QR code scanning
7. NFC (Near Field Communication) support
*Benefits:*
1. Convenience
2. Security
3. Speed
4. Organization
5. Rewards and loyalty programs
6. Easy refunds
7. Reduced transaction fees
*Digital Wallet Providers:*
1. Apple (Apple Pay)
2. Google (Google Pay)
3. PayPal
4. Amazon (Amazon Pay)
5. Samsung (Samsung Pay)
6. Visa (Visa Checkout)
7. Mastercard (Masterpass)
8. American Express (Amex Pay)
*Security Measures:*
1. Encryption
2. Two-factor authentication
3. Password protection
4. Secure sockets layer (SSL)
5. Tokenization
6. Biometric authentication
7. Regular security updates
⭕CREDIT CARDS
Credit cards are payment cards issued by financial institutions, allowing cardholders to borrow funds for purchases, cash advances, and balance transfers.
*Key Definitions:*
1. Credit Limit: Maximum amount cardholder can borrow.
2. Interest Rate (APR): Percentage rate charged on outstanding balance.
3. Fees: Annual, late, foreign transaction, and other charges.
4. Rewards Program: Benefits, such as cashback, points, or travel miles.
5. Introductory Offer: Initial promotional terms, like 0% APR or sign-up bonus.
*Types of Credit Cards:*
1. Cash Back
2. Rewards
3. Travel
4. Balance Transfer
5. Secured
6. Unsecured
7. Business
8. Student
*Credit Card Features:*
1. EMV Chip Technology
2. Contactless Payment
3. Digital Wallet Integration
4. Purchase Protection
5. Building Credit Score
6. Cash Advance Options
7. Travel Insurance
8. Fraud Protection
*Benefits:*
1. Convenience
2. Worldwide Acceptance
3. Rewards and Benefits
4. Purchase Protection
5. Building Credit Score
6. Cash Advance Options
7. Travel Insurance
8. Fraud Protection
*Credit Card Networks:*
1. Visa
2. Mastercard
3. American Express
4. Discover
5. JCB (Japan Credit Bureau)
6. UnionPay
7. Diners Club
*Issuing Banks:*
1. Chase
2. Bank of America
3. Citi
4. Wells Fargo
5. Capital One
6. American Express
7. Discover
8. Barclays
⭕DEBIT CARDS
• a card allowing the holder to transfer money electronically from their bank account when making a purchase.
Debit cards have many features, including:
• Access to funds: Debit cards allow you to use funds from your bank account without withdrawing cash.
• Spending limits: You can set spending limits on your debit card.
• Online payments: You can use your debit card to make online payments, such as shopping online or paying bills.
• Point-of-sale (POS) payments: You can use your debit card to make payments at POS terminals in stores.
• Contactless payments: Some debit cards allow you to make contactless payments.
• Rewards: Some debit cards offer rewards and cashback on your purchases.
• Airport lounge access: Some debit cards may offer access to airport lounges.
• Transaction alerts: You can receive email or SMS alerts about your debit card transactions.
•
• PIN: You need a personal identification number (PIN) to use your debit card.
•
• CVV: Your debit card has a card verification value (CVV) code, which is usually a three-digit number on the back or front of the card.
🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰
⭕RISK IN E PAYMENT SYSTEM
There are many risks associated with electronic payment systems, including:
1.Data breaches
Unauthorized individuals can gain access to sensitive information stored in a digital payment system. This information can be used for fraudulent activities or sold on the dark web.
2.Technical issues
Online payments are vulnerable to technical disturbances that can cause several hours of downtime
3.Legal risk
If you make a payment to an individual or business that fails to deliver the goods or services promised, you may not be able to hold them accountable in court
4.Lack of transparency
A lack of transparency can weaken the reliability of encrypted connections, which can enable security attacks
5.Merchant charges
Merchant accounts can fall into a high-risk profile if the merchant deals in large amounts, multiple currencies, or risk-prone goods. The higher the potential risk, the more expensive the service fees will be.
⭕ Drivers of digital business
Drivers of digital business refer to the key factors, technologies, and trends that enable and accelerate digital transformation and innovation in organizations. These drivers facilitate the creation of new business models, revenue streams, and customer experiences.
Drivers of digital business refer to the key factors, technologies, and trends that enable and accelerate digital transformation and innovation in organizations. These drivers facilitate the creation of new business models, revenue streams, and customer experiences.
*Key Benefits:*
1. Enhanced Customer Experience
2. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
3. Improved Decision-Making
4. New Revenue Streams and Business Models
5. Competitive Advantage
6. Innovation and Growth
⭕BIG DATA ANALYTICS
Video 👇
https://youtu.be/bAyrObl7TYE?si=qtEloLgm2Mjf-Q4o
Big Data Analytics refer to the process of collecting, storing, processing, and analyzing large and complex data sets to gain insights, make informed decisions, and drive business outcomes.
*Big Data:*
Big Data Analytics refer to the process of collecting, storing, processing, and analyzing large and complex data sets to gain insights, make informed decisions, and drive business outcomes.
*Big Data:*
Big Data refers to the vast amounts of structured and unstructured data generated from various sources, including:
1. Social media
2. IoT devices
3. Sensors
4. Transactions
5. Logs
6. Clickstream data
7. Text data
8. Images
9. Videos
⭕ Here are some things to know about big data analytics:
•
• Data sources
Big data can come from a variety of sources, including social media, mobile, email, web, and smart devices.
•
• Data types
Big data can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
•
• Tools
Big data analytics uses tools like business intelligence (BI) systems and tools to help organizations collect and analyze data.
•
• Techniques
Big data analytics uses statistical analysis techniques like clustering and regression, along with newer tools.
•
• Types
There are four main types of big data analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive.
•
• Benefits
Big data analytics can help businesses understand product viability, keep up with trends, and develop and market new products and services.
•
• History
The term "big data" was first used in the mid-1990s to describe the increasing volume of data being stored and used by organizations.
⭕
*Applications of Big Data and Analytics:*
1. Healthcare
2. Finance
3. Retail
4. Marketing
5. Manufacturing
6. Government
7. Transportation
8. Education
⭕ Cloud Computing and StoStorage
*Cloud Computing:*
Cloud computing is a model of delivering computing services over the internet, on-demand and pay-per-use basis.
The delivery of different services through the Internet which includes tools and applications like data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software.
Key Characteristics:
1. On-demand self-service
2. Broad network access
3. Resource pooling
4. Rapid elasticity
5. Measured service
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
On-demand self-service:
-Provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
-Publishes a service catalogue, which contains information about all cloud services available to consumers.
-The service catalogue includes information about service attributes, prices, and request processes.
Broad network access:
-Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms
Measured service:
-Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service
*Cloud Computing Benefits:*
1. Scalability
2. Flexibility
3. Cost-effectiveness
4. Reliability
5. Security
6. Collaboration
7. Automatic software updates
The delivery of different services through the Internet which includes tools and applications like data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software.
*Cloud Storage:*
Cloud storage is a model of storing data online, accessible from anywhere, and scalable.
*Cloud Storage Benefits:*
1. Scalability
2. Accessibility
3. Reliability
4. Security
5. Collaboration
6. Automatic backups
7. Disaster recovery
⭕ Social media
Social media refers to online platforms or tools that allow users to create, share, and interact with content, information, or other users in a virtual environment.
_Key Characteristics:_
1. User-generated content
2. Interactivity and engagement
3. Real-time updates and feedback
4. Social networking and community building
5. Multmedia content (text, images, videos, live streams)
6. Mobile accessibility and optimization
7. Open and collaborative environment
8. Constant evolution and adaptation
⭕The Internet of Things (IoT)
Social media refers to online platforms or tools that allow users to create, share, and interact with content, information, or other users in a virtual environment.
_Key Characteristics:_
1. User-generated content
2. Interactivity and engagement
3. Real-time updates and feedback
4. Social networking and community building
5. Multmedia content (text, images, videos, live streams)
6. Mobile accessibility and optimization
7. Open and collaborative environment
8. Constant evolution and adaptation
⭕The Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data.
The Internet of Things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet
*Key Characteristics:*
1. Interconnected devices
2. Data collection and exchange
3. Automation and control
4. Sensing and actuating capabilities
5. Internet connectivity
6. Real-time data analysis
7. Artificial intelligence and machine learning integration
8. Scalability and flexibility
*IoT Devices:*
1. Smart home devices (thermostats, lights, security cameras)
2. Wearables (smartwatches, fitness trackers)
3. Industrial sensors (temperature, pressure, vibration)
4. Vehicles (connected cars, trucks, drones)
5. Medical devices (implants, wearables, patient monitoring)
6. Smart city infrastructure (traffic management, energy grids)
7. Agricultural sensors (soil moisture, temperature, crop monitoring)
8. Consumer electronics (smart speakers, smart TVs)
*IoT Applications:*
1. Smart homes and buildings
2. Industrial automation and control
3. Transportation and logistics
4. Healthcare and medical monitoring
5. Smart cities and infrastructure
6. Agriculture and farming
7. Energy management and efficiency
8. Retail and customer experience
*IoT Benefits:*
1. Increased efficiency and productivity
2. Improved decision-making with real-time data
3. Enhanced customer experience
4. Reduced energy consumption and costs
5. Increased safety and security
6. Improved healthcare outcomes
7. Increased scalability and flexibility
8. New business models and revenue streams
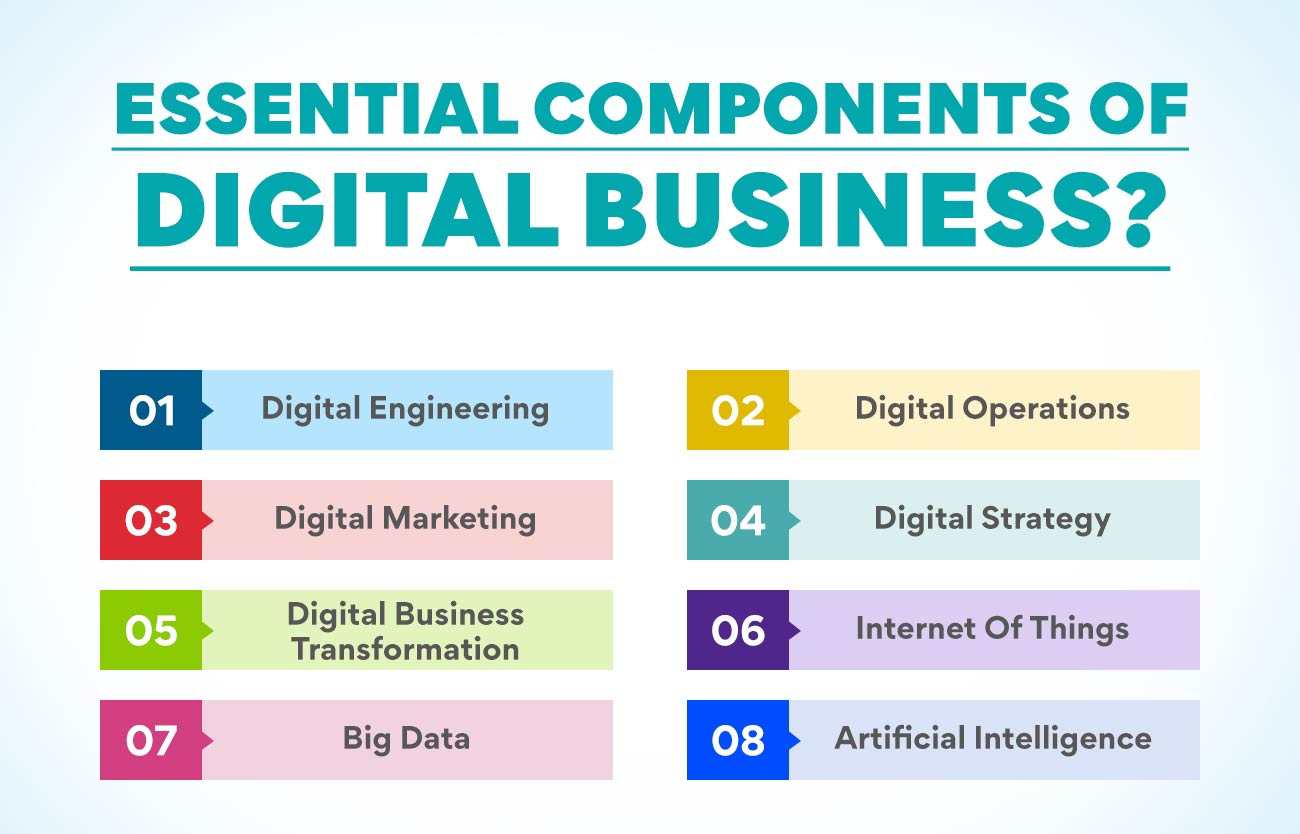
⭕DIGITAL BUSINESS
*Key Characteristics:*
1. Interconnected devices
2. Data collection and exchange
3. Automation and control
4. Sensing and actuating capabilities
5. Internet connectivity
6. Real-time data analysis
7. Artificial intelligence and machine learning integration
8. Scalability and flexibility
*IoT Devices:*
1. Smart home devices (thermostats, lights, security cameras)
2. Wearables (smartwatches, fitness trackers)
3. Industrial sensors (temperature, pressure, vibration)
4. Vehicles (connected cars, trucks, drones)
5. Medical devices (implants, wearables, patient monitoring)
6. Smart city infrastructure (traffic management, energy grids)
7. Agricultural sensors (soil moisture, temperature, crop monitoring)
8. Consumer electronics (smart speakers, smart TVs)
*IoT Applications:*
1. Smart homes and buildings
2. Industrial automation and control
3. Transportation and logistics
4. Healthcare and medical monitoring
5. Smart cities and infrastructure
6. Agriculture and farming
7. Energy management and efficiency
8. Retail and customer experience
*IoT Benefits:*
1. Increased efficiency and productivity
2. Improved decision-making with real-time data
3. Enhanced customer experience
4. Reduced energy consumption and costs
5. Increased safety and security
6. Improved healthcare outcomes
7. Increased scalability and flexibility
8. New business models and revenue streams
⭕DIGITAL BUSINESS
Digital
business refers to the use of digital technologies to create, deliver, and capture value through digital products, services, and experiences._Key Characteristics:_
1. Digitalization of business processes
2. Use of digital technologies (cloud, AI, IoT, blockchain)
3. Online presence and digital channels
4. Data-driven decision-making
5. Digital products and services
6. E-commerce and digital payments
7. Digital marketing and customer engagement
8. Continuous innovation and disruption
⭕ OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES OF DIGITAL BUSINESS ⭕
*Opportunities of Digital Business:*
1. Increased reach and accessibility
2. Improved customer engagement and experience
3. Enhanced data-driven decision-making
4. Increased efficiency and productivity
5. New revenue streams and business models
6. Competitive advantage through innovation
7. Real-time market feedback and adaptation
8. Global market access and expansion
*Challenges of Digital Business:*
1. Cybersecurity threats and data breaches
2. Rapid technological changes and obsolescence
3. Intense competition and market saturation
4. Managing digital transformation and cultural change
5. Ensuring data quality and integrity
6. Balancing personalization and privacy concerns
7. Managing digital risks and liabilities
8. Keeping up with evolving regulatory frameworks
⭕Digital banking
Digital banking, also known as online banking or e-banking, refers to the provision of banking services through digital channels such as the internet, mobile devices, and other electronic platforms.
*Types of Digital Banking:*
1. Online Banking (web-based)
2. Mobile Banking (app-based)
3. Mobile Wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay)
4. Digital-Only Banks (neobanks)
5. Virtual Banking (virtual assistants)
6. Social Media Banking
7. SMS Banking
8. Chatbot Banking
*Digital Banking Services:*
1. Account management (view balances, transactions)
2. Fund transfers (local and international)
3. Bill payments
4. Loan applications
5. Credit card management
6. Investment services
7. Insurance services
8. Financial planning and advisory
*Benefits of Digital Banking:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
⭕ Digital banking
Digital banking, also known as online banking or e-banking, refers to the provision of banking services through digital channels such as the internet, mobile devices, and other electronic platforms.
*Types of Digital Banking:*
1. Online Banking (web-based)
2. Mobile Banking (app-based)
3. Mobile Wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay)
4. Digital-Only Banks (neobanks)
5. Virtual Banking (virtual assistants)
6. Social Media Banking
7. SMS Banking
8. Chatbot Banking
*Digital Banking Services:*
1. Account management (view balances, transactions)
2. Fund transfers (local and international)
3. Bill payments
4. Loan applications
5. Credit card management
6. Investment services
7. Insurance services
8. Financial planning and advisory
*Benefits of Digital Banking:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
⭕ONLINE BANKING
Online banking, also known as internet banking or e-banking, allows users to manage their financial accounts and conduct banking transactions through the internet.
*Benefits of Online Banking:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
*Online Banking Features:*
1. User-friendly interface
2. Secure login and authentication
3. Transaction history and statements
4. Fund transfer and payment options
5. Account alerts and notifications
6. Budgeting and financial planning tools
7. Investment tracking and analysis
8. Customer support and chat services
⭕ MOBILE BANKING
Mobile banking refers to the provision of banking services through mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices.
*Key Features:*
1. Account management
2. Fund transfers
3. Bill payments
4. Loan applications
5. Credit card management
6. Investment services
7. Insurance services
8. Financial planning and advisory
*Benefits:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
⭕TELEBANKING
Telebanking , also known as phone banking, refers to the provision of banking services over the telephone.
*Telebanking Services:*
1. Account balance inquiry
2. Fund transfers
3. Bill payments
4. Loan applications
5. Credit card management
6. Investment services
7. Insurance services
8. Financial planning and advisory
*Benefits of Telebanking:*
1. Convenience (24/7 access)
2. Speed (fast transactions)
3. Cost-effectiveness (lower fees)
4. Accessibility (global reach)
5. Security (advanced encryption)
6. Personalization (customized services)
7. Efficiency (reduced paperwork)
8. Real-time updates
⭕Automatic Clearing House (ACH)
Automatic Clearing House (ACH) is a network that facilitates electronic funds transfers (EFTs) between banks and financial institutions.
*Key Features:*
1. Electronic payment processing
2. Batch processing
3. High-volume transactions
4. Low-cost transactions
5. Secure and reliable
*Types of ACH Transactions:*
1. Direct Deposit (payroll, benefits)
2. Direct Payment (bill payments, tuition)
3. Electronic Checks (e-checks)
4. Recurring Payments (subscriptions, memberships)
5. One-time Payments (online purchases)
⭕ BHIM
BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money) is a mobile payment application developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) to facilitate electronic payments and promote digital transactions in India.
*Key Features:*
1. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) based
2. Scan and Pay using QR code
3. Send and Receive money using Virtual Payment Address (VPA)
4. Bill payments and utility payments
5. Support for multiple languages
6. Integration with various banks
7. Transaction limits: ₹10,000 per transaction, ₹20,000 daily
*Benefits:*
1. Convenient and easy to use
2. Fast and secure transactions
3. No need to carry cash or cards
4. Wide acceptance across merchants
5. Low transaction fees
6. Promotes digital financial inclusion
*Transaction Types:*
1. Person-to-Person (P2P)
2. Person-to-Merchant (P2M)
3. Bill payments
4. Utility payments
5. Online shopping
*Security Features:*
1. Two-factor authentication
2. Encryption
3. Secure socket layer (SSL)
4. Virtual Payment Address (VPA)
5. PIN/password protection
*Participating Banks:*
1. State Bank of India
2. HDFC Bank
3. ICICI Bank
4. Axis Bank
5. Bank of Baroda
6. And many more
⭕UPI
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is a real-time payment system developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) to facilitate inter-bank transactions.
*Key Features:*
1. Instant fund transfers
2. Real-time transactions
3. Single-click payments
4. Virtual Payment Address (VPA)
5. Two-factor authentication
6. Multiple bank account linking
7. Transaction limits: ₹1 lakh per transaction, ₹1 lakh daily
*Benefits:*
1. Convenient and easy to use
2. Fast and secure transactions
3. No need to share bank account details
4. Wide acceptance across merchants
5. Low transaction fees
6. Promotes digital financial inclusion
*Transaction Types:*
1. Person-to-Person (P2P)
2. Person-to-Merchant (P2M)
3. Bill payments
4. Utility payments
5. Online shopping
*Security Features:*
1. Two-factor authentication
2. Encryption
3. Secure socket layer (SSL)
4. Virtual Payment Address (VPA)
5. PIN/password protection
*Participating Banks:*
1. State Bank of India
2. HDFC Bank
3. ICICI Bank
4. Axis Bank
5. Bank of Baroda
6. And many more
*UPI Apps:*
1. BHIM
2. Google Pay
3. PhonePe
4. Paytm
5. Amazon Pay
6. WhatsApp Pay
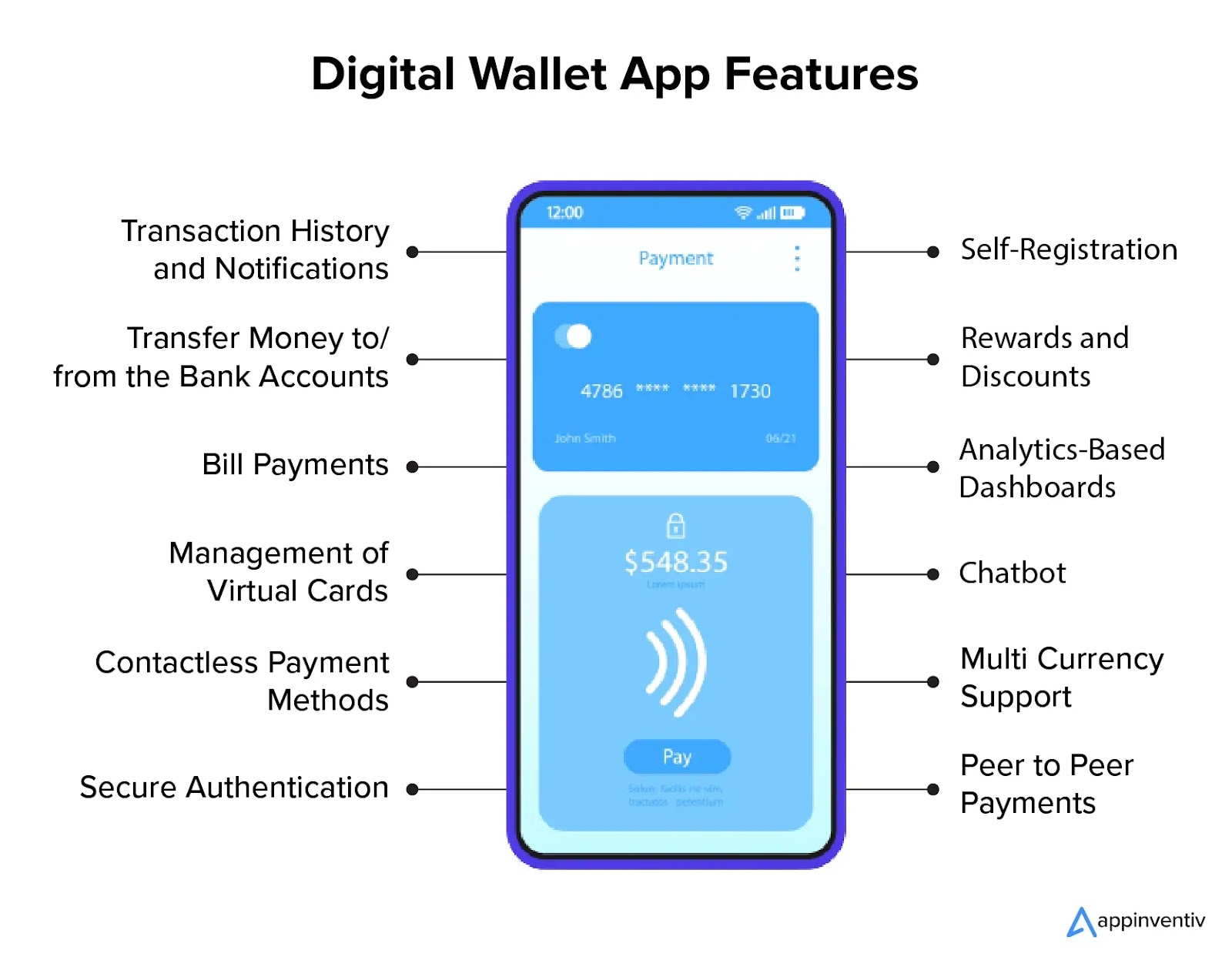
⭕DIGITAL WALLET
A digital wallet, also known as an e-wallet, is a software-based storage solution that securely stores payment information and allows users to make transactions online or offline.
*Types of Digital Wallets:*
1. Mobile wallets (e.g., Apple Pay, Google Pay)
2. Online wallets (e.g., PayPal, Amazon Pay)
3. Desktop wallets (e.g., Bitcoin Core)
4. Hardware wallets (e.g., Ledger, Trezor)
5. Cryptocurrency wallets (e.g., Coinbase, MetaMask)
*Features:*
1. Payment storage (credit/debit cards, bank accounts)
2. Transaction history
3. Password protection
4. Two-factor authentication
5. Encryption
6. QR code scanning
7. NFC (Near Field Communication) support
*Benefits:*
1. Convenience
2. Security
3. Speed
4. Organization
5. Rewards and loyalty programs
6. Easy refunds
7. Reduced transaction fees
*Digital Wallet Providers:*
1. Apple (Apple Pay)
2. Google (Google Pay)
3. PayPal
4. Amazon (Amazon Pay)
5. Samsung (Samsung Pay)
6. Visa (Visa Checkout)
7. Mastercard (Masterpass)
8. American Express (Amex Pay)
*Security Measures:*
1. Encryption
2. Two-factor authentication
3. Password protection
4. Secure sockets layer (SSL)
5. Tokenization
6. Biometric authentication
7. Regular security updates
⭕CREDIT CARDS
Credit cards are payment cards issued by financial institutions, allowing cardholders to borrow funds for purchases, cash advances, and balance transfers.
*Key Definitions:*
1. Credit Limit: Maximum amount cardholder can borrow.
2. Interest Rate (APR): Percentage rate charged on outstanding balance.
3. Fees: Annual, late, foreign transaction, and other charges.
4. Rewards Program: Benefits, such as cashback, points, or travel miles.
5. Introductory Offer: Initial promotional terms, like 0% APR or sign-up bonus.
*Types of Credit Cards:*
1. Cash Back
2. Rewards
3. Travel
4. Balance Transfer
5. Secured
6. Unsecured
7. Business
8. Student
*Credit Card Features:*
1. EMV Chip Technology
2. Contactless Payment
3. Digital Wallet Integration
4. Purchase Protection
5. Building Credit Score
6. Cash Advance Options
7. Travel Insurance
8. Fraud Protection
*Benefits:*
1. Convenience
2. Worldwide Acceptance
3. Rewards and Benefits
4. Purchase Protection
5. Building Credit Score
6. Cash Advance Options
7. Travel Insurance
8. Fraud Protection
*Credit Card Networks:*
1. Visa
2. Mastercard
3. American Express
4. Discover
5. JCB (Japan Credit Bureau)
6. UnionPay
7. Diners Club
*Issuing Banks:*
1. Chase
2. Bank of America
3. Citi
4. Wells Fargo
5. Capital One
6. American Express
7. Discover
8. Barclays
⭕DEBIT CARDS
• a card allowing the holder to transfer money electronically from their bank account when making a purchase.
Debit cards have many features, including:
• Access to funds: Debit cards allow you to use funds from your bank account without withdrawing cash.
• Spending limits: You can set spending limits on your debit card.
• Online payments: You can use your debit card to make online payments, such as shopping online or paying bills.
• Point-of-sale (POS) payments: You can use your debit card to make payments at POS terminals in stores.
• Contactless payments: Some debit cards allow you to make contactless payments.
• Rewards: Some debit cards offer rewards and cashback on your purchases.
• Airport lounge access: Some debit cards may offer access to airport lounges.
• Transaction alerts: You can receive email or SMS alerts about your debit card transactions.
•
• PIN: You need a personal identification number (PIN) to use your debit card.
•
• CVV: Your debit card has a card verification value (CVV) code, which is usually a three-digit number on the back or front of the card.
🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰🔰
⭕E COMMERCPAYMENTS
Ecommerce or "electronic commerce" is the trading of goods and services online. The internet allows individuals and businesses to buy and sell an increasing amount of physical goods, digital goods, and services electronically.
⭕E-Commerce - Business Models
• Business - to - Business (B2B)
• Business - to - Consumer (B2C)
• Consumer - to - Consumer (C2C)
• Consumer - to - Business (C2B)
• Business - to - Government (B2G)
• Government - to - Business (G2B)
• Government - to - Citizen (G2C)
Business - to - Business
A website following the B2B business model sells its products to an intermediate buyer who then sells the product to the final customer.
Business - to - Consumer
A website following the B2C business model sells its products directly to a customer. A customer can view the products shown on the website. The customer can choose a product and order the same.
Consumer - to - Consumer
A website following the C2C business model helps consumers to sell their assets like residential property, cars, motorcycles, etc., or rent a room by publishing their information on the website.
Consumer - to - Business
In this model, a consumer approaches a website showing multiple business organizations for a particular service. The consumer places an estimate of amount he/she wants to spend for a particular service.
Business - to - Government
B2G model is a variant of B2B model. Such websites are used by governments to trade and exchange information with various business organizations.
Government - to - Business
Governments use B2G model websites to approach business organizations. Such websites support auctions, tenders, and application submission functionalities.
Government - to - Citizen
Governments use G2C model websites to approach citizen in general. Such websites support auctions of vehicles, machinery, or any other material. Such website also provides services like registration for birth, marriage or death certificates.
⭕ eCommerce Sales Lifecycle
⭕E-Commerce - Business Models
• Business - to - Business (B2B)
• Business - to - Consumer (B2C)
• Consumer - to - Consumer (C2C)
• Consumer - to - Business (C2B)
• Business - to - Government (B2G)
• Government - to - Business (G2B)
• Government - to - Citizen (G2C)
Business - to - Business
A website following the B2B business model sells its products to an intermediate buyer who then sells the product to the final customer.
Business - to - Consumer
A website following the B2C business model sells its products directly to a customer. A customer can view the products shown on the website. The customer can choose a product and order the same.
Consumer - to - Consumer
A website following the C2C business model helps consumers to sell their assets like residential property, cars, motorcycles, etc., or rent a room by publishing their information on the website.
Consumer - to - Business
In this model, a consumer approaches a website showing multiple business organizations for a particular service. The consumer places an estimate of amount he/she wants to spend for a particular service.
Business - to - Government
B2G model is a variant of B2B model. Such websites are used by governments to trade and exchange information with various business organizations.
Government - to - Business
Governments use B2G model websites to approach business organizations. Such websites support auctions, tenders, and application submission functionalities.
Government - to - Citizen
Governments use G2C model websites to approach citizen in general. Such websites support auctions of vehicles, machinery, or any other material. Such website also provides services like registration for birth, marriage or death certificates.
⭕ eCommerce Sales Lifecycle
Stages
Stage 1: Start-up & fast growth
Most ecommerce businesses go through an initial period of fast and in some cases unexpected growth. This is usually to do with the popularity of the product they sell or market demand rather than the implementation of their ecommerce platforms. Many businesses will choose platforms such as BigCommerce, Shopify or Magento. It's important that your business stays agile and responds quickly to change.
Stage 2: Plateauing growth or consolidation
Businesses reaching this second stage of the ecommerce lifecycle tend to panic and look for quick-fix solutions to perceived issues. You need to understand that it's natural for there to be a levelling off of growth after the early spike. Once your business has gained traction, brand awareness and initial momentum, it's time to reflect on your progress, analyse your data and gain key insights to make measured and strategic changes to your ecommerce website and your marketing.
Stage 3: Renewed growth
Many business owners think that the solution to the issue of plateauing growth is a quick fix or a swift change of direction, which can be an ecommerce platform move or, perhaps, the recruitment of a new ecommerce manager.
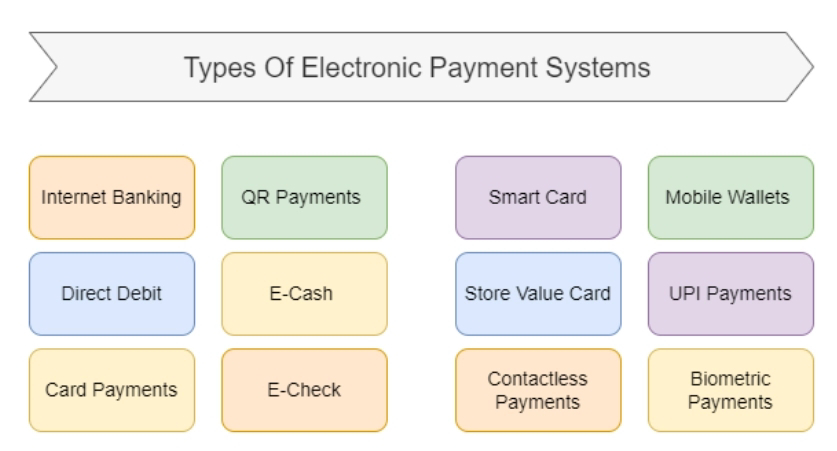
⭕ELECTRONIC PAYMENT SYSTEM
An electronic payment system (e-payment system) is a digital infrastructure that allows people and businesses to transfer money without using cash or checks. E-payment systems use a variety of technologies, including:
• Online banking
• Mobile payment apps
• Electronic point-of-sale terminals
• Credit card payments
• Bank transfers
• Mobile wallets
• Peer-to-peer transfers
• Online payment gateways
⭕ Payment gateways
These act as an interface between a merchant account and an ecommerce website. They capture and transfer payment information from a customer to a bank, and then send the payment acceptance or decline data back to the customer. Some examples of payment gateways include:
•
• PayPal: A popular payment gateway that allows users to send and receive payments using credit cards, debit cards, bank transfers, and PayPal's digital wallet
• Stripe: A payment gateway that supports online payments, subscriptions, and complex payment scenarios
•
• Amazon Pay: A hosted payment gateway that supports major payment methods and credit cards
•
• Authorize.Net:
• A payment gateway that allows users to customize how they process payments
⭕TYPES OF DIGITAL PAYMENTS
Types of Digital Payments In India
1. Banking Cards
Indians widely use banking cards, debit/credit cards, or prepaid cards as an alternative to cash payments. In 1981, the Andhra Bank launched the first credit card in India
2. Unstructured Supplementary Service Data(USSD)
The unstructured supplementary service data (USSD) was launched for those sections of India’s population which do not have access to proper banking and internet facilities.
3. Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS)
The Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS) is a bank-led model for digital payments initiated to leverage the presence and reach of Aadhar. Under this system, customers can use their Aadhaar-linked accounts to transfer money between two Aadhaar-linked bank accounts.
4. Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
The UPI is a payment system that culminates numerous bank accounts into a single application, allowing money transfers between parties.
5. Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets are a type of wallet where you can carry cash in a digital format. Often, customers link their bank accounts or banking cards to their wallets to facilitate secure digital transactions
6. Bank Prepaid Cards
A bank prepaid card is a pre-loaded debit card issued by a bank, usually meant for single use or can be reloaded for multiple uses. It is different from a standard debit card because the latter is always linked to your bank account and can be used numerous times
7.Internet Banking
Internet Banking, also known as e-banking or online banking, allows the customers of a particular bank to make transactions and conduct other financial activities via the bank’s website
8. Mobile Banking
Mobile banking refers to conducting transactions and other activities via mobile devices, typically through the bank’s mobile application (app).
9.Micro ATMs
A micro ATM is a BC device to deliver essential banking services. These correspondents, who could be local store owners, will serve as a ‘micro ATM’ to conduct instant transactions. They will use a device that will let you transfer money via your Aadhaar-linked bank account by merely authenticating your fingerprint.
⭕ Here are some popular electronic payment systems:
*Credit/Debit Card Systems:*
1. Visa
2. Mastercard
3. American Express
4. Discover
5. JCB (Japan Credit Bureau)
6. UnionPay
7. Diners Club
*Digital Wallets:*
1. PayPal
2. Apple Pay
3. Google Pay
4. Amazon Pay
5. Samsung Pay
6. Microsoft Wallet
7. Skrill
*Online Payment Processors:*
1. Stripe
2. Square
3. PayPal Payments Pro
4. (link unavailable)
5. CyberSource
6. WorldPay
7. Adyen
*Bank Transfer Systems:*
1. ACH (Automated Clearing House)
2. Wire Transfer
3. SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area)
4. SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication)
5. Faster Payments
*Cryptocurrency Payment Systems:*
1. Bitcoin
2. Ethereum
3. Litecoin
4. Bitcoin Cash
5. Ripple
6. Dogecoin
7. Dash
*Mobile Payment Systems:*
1. Apple Pay
2. Google Pay
3. Samsung Pay
4. Android Pay
5. Alipay
6. WeChat Pay
7. MobilePay
*E-commerce Payment Platforms:*
1. Shopify Payments
2. Magento Payment Gateway
3. WooCommerce Payments
4. BigCommerce Payments
5. Etsy Payments
6. eBay Payments
7. Amazon Payments
*Contactless Payment Systems:*
1. NFC (Near Field Communication)
2. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)
3. QR Code Payments
4. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
5. Host Card Emulation (HCE)
*Regional Payment Systems:*
1. Alipay (China)
2. WeChat Pay (China)
3. Paytm (India)
4. M-Pesa (Kenya)
5. Sofort (Europe)
6. iDEAL (Netherlands)
7. Giropay (Germany)
⭕A smart card is a plastic card that contains a microprocessor and a memory chip or just a memory chip. The microprocessor card has the ability to add, delete and manipulate information on the card. A memory-chip card, such as a phone card, can only add information.
Uses of smart cards
Smart cards are generally used in applications that must deliver fast, secure transactions. They can protect personal information in numerous situations, including the following:
• credit cards;
• other types of payment cards;
• corporate and government identification cards;
• transit fare payment cards; and
• e-documents, such as electronic passports and visas.
Smart cards, such as debit cards, are often used with a personal identification number (PIN).
An electronic payment system (e-payment system) is a digital infrastructure that allows people and businesses to transfer money without using cash or checks. E-payment systems use a variety of technologies, including:
• Online banking
• Mobile payment apps
• Electronic point-of-sale terminals
• Credit card payments
• Bank transfers
• Mobile wallets
• Peer-to-peer transfers
• Online payment gateways
⭕ Payment gateways
These act as an interface between a merchant account and an ecommerce website. They capture and transfer payment information from a customer to a bank, and then send the payment acceptance or decline data back to the customer. Some examples of payment gateways include:
•
• PayPal: A popular payment gateway that allows users to send and receive payments using credit cards, debit cards, bank transfers, and PayPal's digital wallet
• Stripe: A payment gateway that supports online payments, subscriptions, and complex payment scenarios
•
• Amazon Pay: A hosted payment gateway that supports major payment methods and credit cards
•
• Authorize.Net:
• A payment gateway that allows users to customize how they process payments
⭕TYPES OF DIGITAL PAYMENTS
Types of Digital Payments In India
1. Banking Cards
Indians widely use banking cards, debit/credit cards, or prepaid cards as an alternative to cash payments. In 1981, the Andhra Bank launched the first credit card in India
2. Unstructured Supplementary Service Data(USSD)
The unstructured supplementary service data (USSD) was launched for those sections of India’s population which do not have access to proper banking and internet facilities.
3. Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS)
The Aadhaar Enabled Payment System (AEPS) is a bank-led model for digital payments initiated to leverage the presence and reach of Aadhar. Under this system, customers can use their Aadhaar-linked accounts to transfer money between two Aadhaar-linked bank accounts.
4. Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
The UPI is a payment system that culminates numerous bank accounts into a single application, allowing money transfers between parties.
5. Mobile Wallets
Mobile wallets are a type of wallet where you can carry cash in a digital format. Often, customers link their bank accounts or banking cards to their wallets to facilitate secure digital transactions
6. Bank Prepaid Cards
A bank prepaid card is a pre-loaded debit card issued by a bank, usually meant for single use or can be reloaded for multiple uses. It is different from a standard debit card because the latter is always linked to your bank account and can be used numerous times
7.Internet Banking
Internet Banking, also known as e-banking or online banking, allows the customers of a particular bank to make transactions and conduct other financial activities via the bank’s website
8. Mobile Banking
Mobile banking refers to conducting transactions and other activities via mobile devices, typically through the bank’s mobile application (app).
9.Micro ATMs
A micro ATM is a BC device to deliver essential banking services. These correspondents, who could be local store owners, will serve as a ‘micro ATM’ to conduct instant transactions. They will use a device that will let you transfer money via your Aadhaar-linked bank account by merely authenticating your fingerprint.
⭕ Here are some popular electronic payment systems:
*Credit/Debit Card Systems:*
1. Visa
2. Mastercard
3. American Express
4. Discover
5. JCB (Japan Credit Bureau)
6. UnionPay
7. Diners Club
*Digital Wallets:*
1. PayPal
2. Apple Pay
3. Google Pay
4. Amazon Pay
5. Samsung Pay
6. Microsoft Wallet
7. Skrill
*Online Payment Processors:*
1. Stripe
2. Square
3. PayPal Payments Pro
4. (link unavailable)
5. CyberSource
6. WorldPay
7. Adyen
*Bank Transfer Systems:*
1. ACH (Automated Clearing House)
2. Wire Transfer
3. SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area)
4. SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication)
5. Faster Payments
*Cryptocurrency Payment Systems:*
1. Bitcoin
2. Ethereum
3. Litecoin
4. Bitcoin Cash
5. Ripple
6. Dogecoin
7. Dash
*Mobile Payment Systems:*
1. Apple Pay
2. Google Pay
3. Samsung Pay
4. Android Pay
5. Alipay
6. WeChat Pay
7. MobilePay
*E-commerce Payment Platforms:*
1. Shopify Payments
2. Magento Payment Gateway
3. WooCommerce Payments
4. BigCommerce Payments
5. Etsy Payments
6. eBay Payments
7. Amazon Payments
*Contactless Payment Systems:*
1. NFC (Near Field Communication)
2. RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification)
3. QR Code Payments
4. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
5. Host Card Emulation (HCE)
*Regional Payment Systems:*
1. Alipay (China)
2. WeChat Pay (China)
3. Paytm (India)
4. M-Pesa (Kenya)
5. Sofort (Europe)
6. iDEAL (Netherlands)
7. Giropay (Germany)
⭕A smart card is a plastic card that contains a microprocessor and a memory chip or just a memory chip. The microprocessor card has the ability to add, delete and manipulate information on the card. A memory-chip card, such as a phone card, can only add information.
Uses of smart cards
Smart cards are generally used in applications that must deliver fast, secure transactions. They can protect personal information in numerous situations, including the following:
• credit cards;
• other types of payment cards;
• corporate and government identification cards;
• transit fare payment cards; and
• e-documents, such as electronic passports and visas.
Smart cards, such as debit cards, are often used with a personal identification number (PIN).
⭕RISK IN E PAYMENT SYSTEM
There are many risks associated with electronic payment systems, including:
1.Data breaches
Unauthorized individuals can gain access to sensitive information stored in a digital payment system. This information can be used for fraudulent activities or sold on the dark web.
2.Technical issues
Online payments are vulnerable to technical disturbances that can cause several hours of downtime
3.Legal risk
If you make a payment to an individual or business that fails to deliver the goods or services promised, you may not be able to hold them accountable in court
4.Lack of transparency
A lack of transparency can weaken the reliability of encrypted connections, which can enable security attacks
5.Merchant charges
Merchant accounts can fall into a high-risk profile if the merchant deals in large amounts, multiple currencies, or risk-prone goods. The higher the potential risk, the more expensive the service fees will be.




















Comments
Post a Comment