E COMMERCE INTRODUCTION MODULE 1 NOTES
MODULE 1 INTRODUCTION
📌BUSINESS OPERATIONS
Business operations refer to the day-to-day activities and processes that a company undertakes to produce goods or services, generate revenue, and ensure smooth functioning
Key Features of Business Operations:
- Production:This involves the creation of goods or services, from sourcing raw materials to the final product or service delivery.
- Marketing:This encompasses activities like market analysis, product development, advertising, sales, and customer relationship management to identify and satisfy customer needs.
- Finance:This area manages the company's financial resources, including accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human Resources:This involves managing employees, including recruitment, training, performance management, and compensation.
- Technology:Businesses rely on technology for various operations, including inventory management, customer relationship management, and data analysis.
- Strategic Planning:This involves setting long-term goals and developing plans to achieve them, ensuring all business functions are aligned.
- Compliance:Businesses must adhere to relevant laws and regulations, ensuring they operate within legal and ethical boundaries.
- Cost Control:Managing expenses effectively to ensure profitability and financial stability. .
Key elements of business operations 1.processes,
2.people,
3. technology,
4.location
5.information & data.
These elements work together to ensure a business can efficiently produce goods or services, manage its resources, and meet customer needs.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
1. Processes:
These are the workflows and procedures that guide how work is done within a business.
Well-defined processes ensure consistency, efficiency, and quality in operations.
2. People:
This includes the employees, contractors, and anyone else who contributes to the business's operations.
The skills, experience, and motivation of the workforce directly impact productivity and success.
3. Technology and Equipment:
This encompasses the tools, software, and machinery used to support business operations.
Importance:
.
4. Location:
This refers to the physical or virtual space where the business operates.
Location can influence access to resources, customer proximity, and operational costs.
5. Information and Data:
This includes all the data collected and used by the business to make informed decinternet.
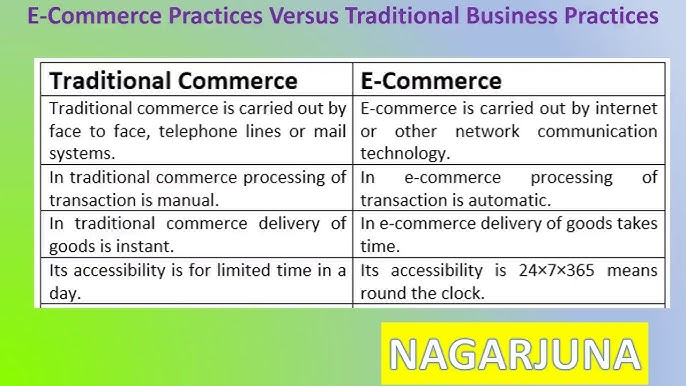
TRADITIONAL COMMERCE
Traditional commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods or services through face-to-face interactions in physical locations, such as stores, markets, or shops, without the use of the internet
Disadvantages limitations of traditional commerce
1. Limited Reach and Market Expansion:
- Traditional businesses are often restricted to a local or regional market, limiting their potential customer base.
2. Higher Operational Costs:
- Maintaining a physical store involves rent, utilities (electricity, water, etc.), and property taxes.
- 3. Time-Consuming for Customers:
- Customers need to travel to the store, which can be time-consuming and inconvenient, especially for those with limited mobility or busy schedules.
4. Limited Operating Hours:
- Physical stores have fixed operating hours, limiting customers' ability to shop at their convenience.
5. Slower Adaptation to Technology:
- Traditional businesses may face challenges in adopting and integrating new technologies, potentially falling behind competitors who leverage digital platforms.
6. Inventory Management Challenges:
- Physical inventory management can be complex and prone to errors, leading to stockouts, overstocking, or inaccurate inventory records.
7. Dependence on Physical Infrastructure:
- Traditional businesses rely heavily on physical infrastructure, which can be vulnerable to disruptions (e.g., power outages, natural disasters).
- .
8. Limited Personal Interaction in Some Cases:
- While some traditional businesses excel at personalized customer service, others may struggle to provide the same level of interaction and rapport as online businesses that use chatbots and other digital tools.
ORIGIN OF E COMMERCE
Eletronic commerce, originated with the use of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) in the 1960s, primarily by large corporations for exchanging data and facilitating transactions. The development of the internet and the World Wide Web in the 1990s, along with the introduction of online payment methods, marked a significant shift towards the modern form of e-commerce.
👇Key Growth Drivers:
1.Internet and Smartphone Penetration:
The expanding access to the internet and smartphones is a major catalyst for e-commerce growth.
2.Digital Payments:
The adoption of digital payment methods like UPI has simplified online transactions and contributed to the sector's expansion.
3.Government Initiatives:
Government support, including the launch of digital payment platforms like BHIM UPI and initiatives like Startup India, has fostered a favorable environment for e-commerce businesses.
4.Increased Consumer Spending:
As consumer wealth increases and spending power grows, there is a greater demand for online shopping.
5.Rise of Emerging Technologies:
Technologies like AI, machine learning, are enhancing the online shopping experience, leading to more personalized and immersive interactions.
6.Diversification of Categories:
E-commerce is expanding beyond traditional categories like electronics and apparel to include groceries, personal care, beauty, and wellness products, among others.
BASIC TECHNOLOGIES OF E COMMERCE
1. *Web development*: Building e-commerce websites and applications.
2. *Payment gateways*: Secure online payment processing.
3. *Database management*: Storing and managing customer data, product information, and orders.
4. *E-commerce platforms*: Pre-built solutions for creating and managing online stores.
5. *Security measures*: Protecting customer data and preventing cyber threats.
6. *Digital marketing*: Promoting e-commerce businesses and attracting customers.
These technologies enable e-commerce businesses to operate efficiently and provide a great customer experience.
👉Features / characteristics/ Advantages/ Merits of e commerce
1. Global Reach
```* E-commerce allows businesses to reach a global audience, increasing their customer base and sales potential.
```
2. 24/7 Availability
```* Online stores are open 24/7, enabling customers to shop at their convenience.
```
3. Convenience
```* E-commerce provides customers with the convenience of shopping from anywhere, at any time, and on various devices.
```
4. Wide Product Range
```* Online stores can offer a wide range of products, including niche and specialty items.
```
5. Easy Comparison
```* Customers can easily compare prices, features, and reviews of different products.
```
6. Personalization
```* E-commerce platforms can offer personalized recommendations and offers based on customer behavior and preferences.
```
7. Secure Payment Options
```* E-commerce platforms provide secure payment options, protecting customer financial information.
```
8. Order Tracking
```* Customers can track their orders in real-time, improving the overall shopping experience.
```
9. Customer Reviews
```* Customers can leave reviews and ratings, helping others make informed purchasing decisions.
```
10. Cost-Effective
```* E-commerce can be more cost-effective than traditional brick-and-mortar stores, reducing overhead costs.
```
11. Scalability
```* E-commerce platforms can easily scale to accommodate growing customer bases and sales volumes.
```
12. Data Analysis
```* E-commerce platforms provide valuable insights into customer behavior, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Limitations of E-commerce:
1.Security Risks:
Data breaches and online fraud are major concerns that can damage customer trust and lead to financial losses.
2.Intense Competition:
The online marketplace is highly competitive, making it challenging to stand out and attract customers.
3.Lack of Personal Interaction:
The absence of face-to-face interaction can make it difficult to build relationships with customers and provide personalized support.
4.Dependence on Technology:
E-commerce relies heavily on technology, and technical issues like website downtime can disrupt sales.
I. User:
This may be individual / organization or anybody using the e-commerce platforms
2.E-commerce Vendors:
This is the organization/ entity providing the user, goods/ services. E.g.: www.flipkart.com.
3.Technology Infrastructure:
This includes Server computers apps etc.
4.Internet / Network:
This is the key to success of e-commerce transactions.
Internet connectivity is important for any e-commerce transaction to go through.
5.Web portal:
This shall provide the interface through which an individual/organization shall perform e-commerce transactions.
6.Payment Gateway:
The payment mode through which customers shall make payments. Payment gateway represents the way e-commerce / m-commerce vendors collects their payments.
🔽TYPES OF E COMMERCE 🔽
E-commerce, or electronic commerce, encompasses various business models that facilitate online transactions. These models can be broadly categorized into six main types: Business-to-Business (B2B), Business-to-Consumer (B2C), Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C), Consumer-to-Business (C2B), Business-to-Government (B2G), and Consumer-to-Government (C2G).
1.B2B (Business-to-Business):
This model involves electronic transactions between businesses. Examples include a manufacturer selling raw materials to another company or a wholesaler selling products to a retailer.
2.B2C (Business-to-Consumer):
This is the most common type of e-commerce, where businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers. Examples include online retailers like Amazon and Flipkart, according to IndiaFilings.
3.C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer):
This model facilitates online transactions between individual consumers. Examples include online marketplaces like eBay or platforms like Craigslist where individuals can sell items to each other.
4.C2B (Consumer-to-Business):
In this model, individuals offer products or services to businesses. An example would be a freelance graphic designer selling their services to a company.
5.B2G (Business-to-Government):
This model involves businesses selling products or services to government entities. This often involves more complex processes and regulations compared to other models.
6.C2G (Consumer-to-Government):
This model focuses on online transactions between individuals and government agencies. Examples include paying taxes online or applying for government services through online portals.











Comments
Post a Comment